Last Updated on July 4, 2024 by Arnav Sharma
In the world of technology, acronyms are thrown around like confetti. With so many options available, it can be challenging to understand the differences between them. SAAS, PAAS, and IAAS are three such terms that often leave people scratching their heads. These terms are used in the cloud computing industry to describe different types of services that are offered. Each of these services has its own unique characteristics, benefits, and drawbacks.
Introduction to SAAS, PAAS, and IAAS
In the ever-evolving landscape of technology, understanding the various cloud computing models can be quite daunting. Amidst the jargon and acronyms, three terms stand out – SAAS, PAAS, and IAAS. These models have revolutionized the way businesses operate and utilize technology resources. But what exactly do these terms mean?
Firstly, let’s delve into SAAS, which stands for Software as a Service. This model allows users to access and use software applications over the internet, eliminating the need for traditional software installations and maintenance. SAAS provides a convenient and cost-effective solution for businesses as they can access powerful software tools without the hassle of managing servers or infrastructure.
Moving on to PAAS, or Platform as a Service, this model offers a comprehensive development platform to create, test, and deploy various applications. With PAAS, developers can focus solely on building and optimizing their applications, without worrying about underlying infrastructure management. By leveraging PAAS, businesses can streamline their development processes and accelerate time-to-market for their applications.
Lastly, IAAS, which stands for Infrastructure as a Service, provides businesses with virtualized computing resources over the internet. With IAAS, organizations have the flexibility to scale their infrastructure up or down as per their requirements, without the need for physical hardware investments. This model empowers businesses to have complete control over their infrastructure, including servers, storage, and networking, while eliminating the burden of infrastructure maintenance.
Understanding the differences between SAAS, PAAS, and IAAS
SAAS, or Software as a Service, refers to cloud-based software applications that are hosted and managed by a third-party provider. With SAAS, users can access and use software applications through the internet without the need for local installation or maintenance. Popular examples of SAAS include customer relationship management (CRM) platforms like Salesforce, collaboration tools like Google Docs, and project management software like Asana.
PAAS, or Platform as a Service, takes things a step further by providing a complete development and deployment environment for developers. With PAAS, developers can build, test, and deploy applications without having to worry about infrastructure management. PAAS platforms provide an easy-to-use interface and pre-configured frameworks that streamline the development process. Popular PAAS providers include Google App Engine, Microsoft Azure, and Heroku.
IAAS, or Infrastructure as a Service, focuses on the provision of virtualized computing resources over the internet. With IAAS, businesses can rent virtualized servers, storage, and networking infrastructure from a cloud provider. This gives them the flexibility to scale resources up or down based on their needs. Examples of IAAS providers include Amazon Web Services (AWS), Microsoft Azure, and Google Cloud Platform.
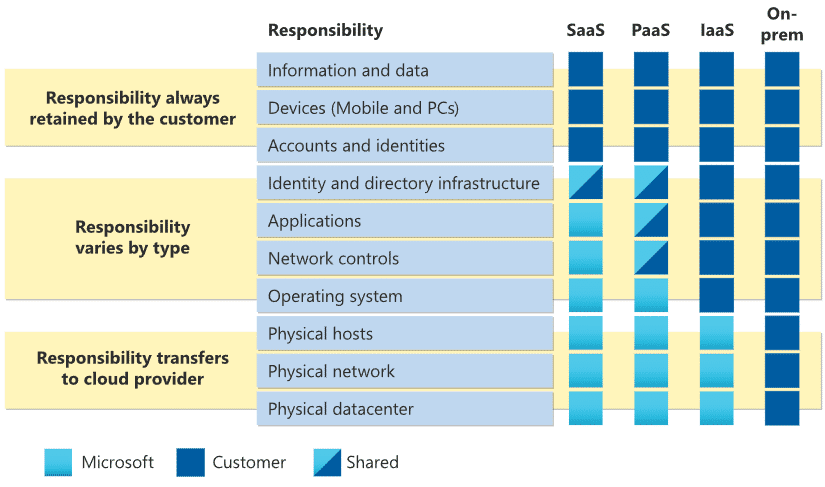
While SAAS, PAAS, and IAAS all fall under the umbrella of cloud computing, they differ in terms of the level of service and the responsibilities of the users and providers. SAAS offers ready-to-use software applications, PAAS provides a platform for application development, and IAAS offers flexible infrastructure resources.
Key features and benefits of SAAS
Software as a Service (SAAS) has revolutionized the way businesses operate and deliver their services. With SAAS, businesses can access and use software applications hosted in the cloud, eliminating the need for costly infrastructure and technical expertise. Let’s explore some key features and benefits of SAAS.
1. Accessibility and Convenience: SAAS applications can be accessed from anywhere, at any time, as long as there is an internet connection. This allows businesses to work remotely, collaborate with team members across different locations, and provide seamless access to customers.
2. Cost Savings: SAAS eliminates the need for upfront capital investments in hardware, software, and infrastructure. With a subscription-based pricing model, businesses can pay for the software on a monthly or annual basis, reducing operational costs and enabling predictable budgeting.
3. Scalability: SAAS offers scalability to accommodate the changing needs of businesses. As your business grows, you can easily scale up or down the usage of the software without worrying about capacity constraints or hardware limitations.
4. Automatic Updates and Maintenance: SAAS providers take care of software updates, security patches, and system maintenance, ensuring that businesses are always using the latest version of the software without any hassle. This saves time and resources spent on manual updates and maintenance.
5. Integration and Compatibility: SAAS applications are designed to integrate with other software systems, providing seamless data flow and interoperability. This enables businesses to streamline their operations, automate workflows, and improve overall efficiency.
6. Security and Data Protection: SAAS providers invest heavily in robust security measures to protect sensitive data. They employ industry-standard encryption, multi-factor authentication, and regular backups to ensure data integrity and safeguard against cyber threats.
7. Flexibility and Customization: SAAS applications often offer customization options to tailor the software to specific business needs. This allows businesses to adapt the software to their workflows, branding, and industry requirements, enhancing user experience and productivity.
Use cases and industries where SAAS is commonly used
Software as a Service (SAAS) has revolutionized the way businesses operate across various industries. Its flexibility, scalability, and cost-effectiveness have made it a popular choice for companies of all sizes. Let’s explore some of the common use cases and industries where SAAS is commonly utilized.
1. Customer Relationship Management (CRM):
SAAS-based CRM platforms have become essential for businesses looking to streamline their sales, marketing, and customer service processes. Companies can easily access customer data, track interactions, and manage relationships all in one centralized system. Popular SAAS CRM solutions include Salesforce, HubSpot, and Zoho CRM.
2. Human Resources (HR) and Talent Management:
SAAS HR solutions have simplified the hiring, onboarding, and management of employees. These platforms offer features like applicant tracking, performance management, payroll processing, and employee self-service portals. Companies like Workday, BambooHR, and ADP provide robust SAAS HR solutions across industries.
3. Project Management and Collaboration:
SAAS project management tools enable teams to collaborate, track progress, and manage tasks efficiently. Whether it’s Agile project management or simple task management, SAAS platforms like Asana, Trello, and Basecamp provide intuitive interfaces and robust features to keep teams organized and productive.
4. Marketing Automation:
SAAS marketing automation tools help businesses automate their marketing campaigns, lead generation, and customer engagement strategies. These platforms offer features such as email marketing, lead nurturing, social media management, and analytics. Popular SAAS marketing automation solutions include Marketo, Mailchimp, and HubSpot Marketing Hub.
5. E-commerce:
SAAS-based e-commerce platforms have simplified the process of setting up and managing online stores. These platforms offer features like product catalog management, secure payment gateways, inventory management, and order processing. Shopify, BigCommerce, and WooCommerce are widely used SAAS e-commerce solutions.
6. Financial Management:
SAAS financial management tools provide businesses with a streamlined approach to managing their finances, including budgeting, invoicing, expense tracking, and financial reporting. QuickBooks, Xero, and FreshBooks are popular SAAS solutions in this space.
Exploring the capabilities and advantages of PAAS
Platform as a Service (PAAS) is a cloud computing model that provides developers with a platform to build, deploy, and manage applications without the need to worry about the underlying infrastructure. PAAS offers a comprehensive set of tools and services that enable developers to focus solely on the application development process, rather than managing servers, operating systems, and other infrastructure components.
One of the key advantages of PAAS is its ability to streamline the development process. With PAAS, developers can leverage pre-built components, frameworks, and libraries to accelerate application development. This not only saves time but also allows developers to focus on writing code that adds value to their applications.
Moreover, PAAS offers a scalable and elastic infrastructure. It allows developers to easily scale their applications based on demand, whether it’s handling a sudden surge in traffic or accommodating growth over time. This eliminates the need to provision and manage resources manually, as the PAAS provider takes care of the underlying infrastructure and ensures that the application has the necessary resources to operate efficiently.
Another advantage of PAAS is its inherent flexibility. It supports multiple programming languages and frameworks, allowing developers to choose the tools that best suit their needs and preferences. This flexibility empowers developers to work with familiar technologies and leverage their existing skills, leading to increased productivity and reduced learning curves.
Additionally, PAAS provides robust security and compliance features. PAAS providers invest heavily in security measures, ensuring that applications and data are protected against potential threats. They also offer various compliance certifications, making it easier for businesses to meet industry-specific regulatory requirements.
Lastly, PAAS offers seamless integration with other cloud services. It enables developers to leverage additional cloud services such as databases, storage, messaging, and analytics, further enhancing the capabilities of their applications. This integration allows for a more cohesive and comprehensive cloud strategy, enabling organizations to optimize their operations and deliver enhanced user experiences.
Real-world examples of PAAS applications and scenarios
PAAS, or Platform as a Service, offers developers a platform to build, test, and deploy applications without worrying about the underlying infrastructure. To better understand how PAAS is used in real-world scenarios, let’s take a look at some examples.
1. Heroku: This cloud-based PAAS platform is widely used by developers for deploying web applications. With Heroku, developers can focus on writing code and let the platform handle tasks like scaling, load balancing, and infrastructure management. It offers a seamless deployment experience and supports multiple programming languages, making it a popular choice for startups and small businesses.
2. Google App Engine: This PAAS offering from Google allows developers to build and host web applications using Google’s infrastructure. It supports various programming languages, including Python, Java, and Node.js, and provides auto-scaling capabilities, ensuring that applications can handle increased traffic without manual intervention. With Google’s robust infrastructure and easy integration with other Google Cloud services, App Engine is an attractive choice for developers.
3. Microsoft Azure: Azure is a comprehensive cloud computing platform that offers a range of services, including PAAS. With Azure App Service, developers can build, deploy, and scale web applications effortlessly. It supports popular programming languages like .NET, Java, and Python, and provides features like autoscaling, continuous deployment, and integration with other Azure services. Azure’s extensive documentation, developer tools, and integration capabilities make it a strong contender in the PAAS space.
4. Salesforce Platform: Designed specifically for building enterprise applications, the Salesforce Platform (formerly known as Force.com) is a PAAS offering that enables developers to create customized applications on top of Salesforce CRM. It provides a powerful set of tools, including a visual development environment, database management, and integration capabilities. The platform’s scalability and flexibility make it suitable for businesses of all sizes, particularly those looking to extend the functionality of the Salesforce ecosystem.
IAAS explained: Infrastructure as a Service
Infrastructure as a Service (IaaS) is a cloud computing model that provides virtualized computing resources over the internet. With IaaS, businesses can build and manage their own virtual data centers without the need for physical infrastructure or on-premises hardware.
In simple terms, IaaS allows businesses to rent virtualized servers, storage, and networking infrastructure from a cloud provider, eliminating the need to invest in costly hardware and maintenance. This model offers immense flexibility and scalability, as resources can be easily scaled up or down based on the business’s needs.
With IaaS, businesses have complete control over their infrastructure. They can deploy and manage their own operating systems, applications, and databases, giving them the freedom to customize their environment as they see fit. This makes IaaS particularly attractive for businesses with specific requirements or complex IT infrastructures.
Additionally, IaaS providers handle the maintenance and management of the underlying hardware, ensuring high availability and reliability. This allows businesses to focus on their core competencies and allocate their resources more effectively.
Some popular examples of IaaS providers include Amazon Web Services (AWS), Microsoft Azure, and Google Cloud Platform. These providers offer a wide range of services, including virtual machines, storage solutions, load balancers, and networking capabilities, among others.
Comparing the pros and cons of SAAS, PAAS, and IAAS
When it comes to cloud computing, three major models dominate the market: Software as a Service (SaaS), Platform as a Service (PaaS), and Infrastructure as a Service (IaaS). Understanding the pros and cons of each model is crucial in determining which one best suits your business needs.
Starting with SaaS, this model offers ready-to-use software applications hosted by a provider, eliminating the need for you to manage infrastructure or software updates. The key advantage is the ease of deployment and accessibility from any device with an internet connection. SaaS also offers scalability, allowing you to easily adjust your subscription based on your needs. However, customization options may be limited, and you are reliant on the service provider for updates and security.
Moving on to PaaS, this model provides a platform for developers to build, test, and deploy applications. It offers a higher level of control and flexibility compared to SaaS, as you have the ability to customize and configure the platform to suit your specific requirements. PaaS also simplifies the development process by providing tools and frameworks. However, PaaS may not be suitable for businesses with complex or highly specific needs, as it operates within the constraints of the platform provided by the service provider.
Lastly, IaaS provides virtualized computing resources such as virtual machines, storage, and networks. With IaaS, you have the most control over your infrastructure, allowing for complete customization and flexibility. This model is ideal for businesses with specific hardware and software requirements. However, managing the infrastructure requires technical expertise and ongoing maintenance, making it more suitable for businesses with dedicated IT teams.
Factors to consider when choosing between SAAS, PAAS, and IAAS
When it comes to choosing between SAAS, PAAS, and IAAS, there are several important factors to consider. Each option offers unique benefits and considerations that can greatly impact your business operations.
1. Scalability: Consider the scalability needs of your business. SAAS solutions are typically the most scalable option as they offer ready-to-use software applications that can be easily scaled up or down based on your business needs. PAAS provides a platform for developers to build and deploy applications, offering some scalability but with more flexibility and control. IAAS, on the other hand, offers the highest level of scalability as it provides virtualized infrastructure resources that can be easily expanded or contracted as required.
2. Customization: Evaluate the level of customization you require for your business. SAAS solutions are often pre-built and offer limited customization options. PAAS allows for greater customization as developers have more control over the underlying infrastructure and can tailor applications to specific needs. IAAS provides the highest level of customization as it offers complete control over the infrastructure, allowing businesses to build and manage their own virtualized environment.
3. Cost: Consider the cost implications of each option. SAAS solutions typically involve subscription-based pricing models, where businesses pay a recurring fee for using the software application. PAAS often involves a combination of subscription fees and usage-based charges for resources consumed. IAAS typically follows a pay-as-you-go model, where businesses are billed based on the resources utilized. Evaluate your budget and projected usage to determine which option aligns with your financial goals.
4. Technical expertise: Assess the technical expertise available within your organization. SAAS solutions require minimal technical expertise as they are ready to use out of the box. PAAS requires a higher level of technical proficiency as developers need to build and deploy applications on the platform. IAAS demands the most technical expertise as businesses are responsible for managing and maintaining the virtualized infrastructure.
5. Security and compliance: Consider the security and compliance requirements of your business. SAAS solutions often provide robust security measures as they are managed by the service provider. PAAS and IAAS require businesses to take a more active role in implementing security measures and ensuring compliance with industry regulations. Evaluate the level of control and responsibility you have over data security and compliance when choosing between the options.
Making the right choice for your business or project
In conclusion, understanding the differences between SAAS, PAAS, and IAAS is crucial in making the right choice for your business or project.
SAAS, or Software as a Service, offers a ready-to-use software application that is accessed over the internet. This model is ideal for businesses looking for a hassle-free solution without the need for infrastructure management. It provides convenience and flexibility, allowing businesses to focus on their core competencies while relying on the software provider for maintenance and updates.
PAAS, or Platform as a Service, provides a platform for developers to build, test, and deploy applications. It offers a complete development environment with tools and resources, making it suitable for businesses that require customization and control over their application development process. With PAAS, businesses can benefit from scalability, reduced development time, and efficient collaboration among team members.
IAAS, or Infrastructure as a Service, offers virtualized computing resources such as servers, storage, and networking. It provides businesses with the flexibility to configure and manage their own infrastructure, making it ideal for organizations with specific hardware and software requirements. IAAS offers scalability, cost-effectiveness, and control, allowing businesses to scale their infrastructure based on their needs.
When choosing between SAAS, PAAS, and IAAS, consider factors such as your business requirements, technical expertise, scalability needs, and budget. Assess the level of control, customization, and maintenance you require, as well as the scalability and flexibility you need for future growth.
Q: What is the difference between SAAS, PAAS, and IAAS?
A: SAAS, PAAS, and IAAS are different types of cloud computing service models. SAAS stands for Software as a Service, PAAS stands for Platform as a Service, and IAAS stands for Infrastructure as a Service.
Q: How do SAAS vs PAAS vs IAAS differ?
A: SAAS provides software applications over the internet, while PAAS provides a platform for developing, testing, and deploying applications, and IAAS provides virtualized computing resources such as virtual machines.
Q: What is cloud computing service?
A: Cloud computing is the delivery of computing services over the internet, including storage, databases, software, and servers, without the need for on-premises infrastructure.
Q: What is a cloud service provider?
A: A cloud service provider is a company that offers cloud computing services and resources, such as storage, servers, and applications, to businesses and individuals.
Q: What is a service model in cloud computing?
A: A service model in cloud computing refers to the type of cloud service being provided, such as SAAS, PAAS, or IAAS.
Q: How can I use IAAS?
A: You can use IAAS by accessing virtualized computing resources, such as virtual machines, storage, and networks, over the internet through a cloud service provider.
Q: What is a common example of SAAS (software as a service)?
A: A common example of SAAS is Adobe Creative Cloud, which provides software applications such as Photoshop and Illustrator over the internet.
Q: What is the difference between IAAS vs SAAS?
A: The main difference between IAAS and SAAS is that IAAS provides virtualized computing infrastructure, while SAAS provides software applications.
Q: What are the main types of cloud computing?
A: The main types of cloud computing are SAAS, PAAS, and IAAS.
Q: What are some examples of SAAS products?
A: Some examples of SAAS products are Salesforce, Gmail, and Dropbox, which provide software applications over the internet.
keywords: cloud service model in cloud infrastructure use paas and saas hybrid cloud in ibm cloud saas app of aws elastic and aws elastic beanstalk saas service in private cloud iaas include paas solution iaas vs paas vs saas