Last Updated on May 18, 2024 by Arnav Sharma
SSDs, or Solid-State Drives, have become the gold standard for modern data storage due to their superior performance and reliability. Unlike traditional hard drives (HDDs), which use spinning disks to read and write data, SSDs use NAND flash memory chips, offering significantly faster read and write speeds. This solid-state technology has revolutionized how we think about data storage, making SSDs a preferred choice for many consumers and professionals.
What is eMMC Storage?
Embedded MultiMediaCard (eMMC) storage is another type of flash storage commonly found in budget laptops, tablets, and smartphones. Like SSDs, eMMC storage uses NAND flash memory, but the architecture and functionality differ. eMMC is an embedded storage solution, meaning it is soldered directly onto the motherboard of a device, making it a more integrated and cost-effective option.
eMMC vs. SSD: Key Differences
Performance
One of the primary differences between eMMC and SSD is performance. SSDs, especially NVMe SSDs, offer much higher read and write speeds compared to eMMC. This performance boost is due to the advanced flash memory controller integrated into SSDs, which allows for faster data processing and retrieval. While eMMC storage is adequate for basic tasks, SSDs provide superior performance for demanding applications and multitasking.
Storage Capacities
When it comes to storage capacities, SSDs generally offer a broader range of options, from 120GB to several terabytes. In contrast, eMMC storage is typically found in lower capacities, usually between 32GB and 128GB. This difference makes SSDs a better choice for users who require more storage space for their files and applications.
Usage Scenarios
eMMC storage works best in devices where cost and space are primary considerations, such as budget laptops, tablets, and some smartphones. Its low-cost nature and integration make it ideal for these applications. On the other hand, SSDs are preferred in scenarios where performance and storage capacity are critical, such as in gaming laptops, high-end PCs, and workstations.
Replacing eMMC with SSD
Many users wonder if they can replace eMMC storage with an SSD. In most cases, this is not possible because eMMC is soldered onto the motherboard. However, if your device supports additional storage options like an M.2 slot, you can add an SSD to enhance performance and storage capacity.
Why Choose SSD Over eMMC?
Choosing an SSD over eMMC comes down to performance and storage needs. SSDs offer better performance and more significant storage capacities, making them ideal for intensive tasks and large data storage. For users looking for a quick and reliable storage solution, SSDs are the way to go.
SSD Storage Options
SSDs come in various forms, including SATA SSDs and NVMe SSDs. SATA SSDs, though slower than NVMe SSDs, still offer substantial improvements over traditional HDDs. NVMe SSDs use the PCIe interface, providing even faster read and write speeds, making them the top choice for users seeking the best performance.
Flash Storage Technologies
Both eMMC and SSD storage technologies use NAND flash memory, but the implementation and performance vary. eMMC offers a more integrated and cost-effective solution, while SSDs, with their advanced flash memory controllers and higher capacities, provide superior performance.
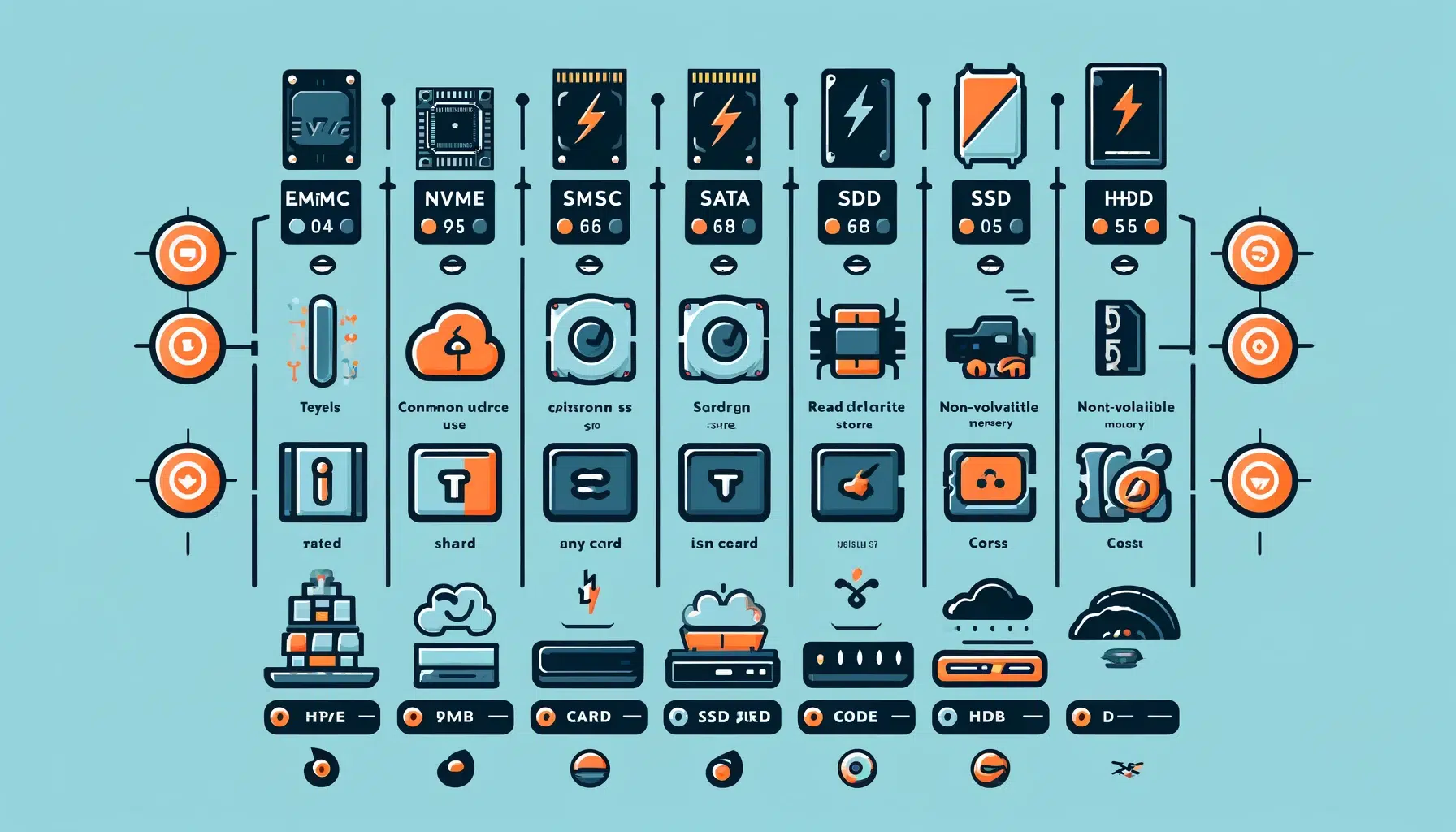
Overall Comparison:
Storage Comparison
| Feature | eMMC Drive | NVMe SSD | SATA SSD | HDD | SD Card | USB Flash Drives | Cloud Storage |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Storage Type | Internal Storage | Internal Storage | Internal Storage | Internal Storage | Removable Storage | Removable Storage | Remote Storage |
| Common Use Case | Budget Laptop or Tablet | High-performance Laptop/PC | Standard Laptop/PC | Desktop/Backup | Cameras, Phones | Data Transfer, Backup | Online Data Access |
| Memory and a Flash Memory | NAND Flash Chips | NAND Flash Chips | NAND Flash Chips | Magnetic Disks | NAND Flash Memory | NAND Flash Memory | N/A |
| Read/Write Speed | Moderate | Very Fast | Fast | Slow | Moderate | Moderate | Variable |
| Fast is eMMC Storage | Yes | Faster than eMMC | Faster than eMMC | No | No | No | N/A |
| Bulk Storage | No | Yes | Yes | Yes | No | No | Yes |
| Non-volatile Memory | Yes | Yes | Yes | No | Yes | Yes | N/A |
| Popular Storage | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes |
| Low-cost Nature of eMMC Storage | Yes | No | No | Yes | Yes | Yes | N/A |
| SSD Without Much Cost | No | No | Yes | N/A | N/A | N/A | N/A |
| Drive or SD Card | No | No | No | Yes | Yes | Yes | N/A |
| HDD vs SSD | N/A | SSD Stands | SSD Stands | HDD Stands | N/A | N/A | N/A |
| Storage Commonly Used | Laptops, Tablets | High-end PCs, Gaming Laptops | General PCs, Laptops | Desktops, Backup | Cameras, Mobile Devices | General Use, Backup | Access Anywhere |
| Internal Storage | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | No | No | N/A |
| Better Than SSD | No | N/A | N/A | No | No | No | N/A |
| Data Storage System | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes |
| Type of Storage | Embedded | Internal PCIe | Internal SATA | Internal | Removable | Removable | Remote |
| Storage Device | eMMC Chip | NVMe SSD | SATA SSD | HDD | SD Card | USB Flash Drive | Cloud Storage |
| Laptop Storage | Yes | Yes | Yes | No | No | No | Yes |
| SATA SSD vs NVMe SSD | N/A | Faster | Slower | N/A | N/A | N/A | N/A |
| What’s the Difference? | Integrated, Low Cost | Highest Speed, High Cost | Balanced Speed, Moderate Cost | High Capacity, Low Speed | Portable, Small Capacity | Portable, Small Capacity | Access Anywhere, Subscription |
FAQ:
Q: How fast is eMMC storage compared to other types?
A: eMMC storage offers solid-state storage without much complexity, providing adequate speed for everyday tasks.
Q: What type of storage is commonly used in modern devices?
A: Solid-state storage is commonly used, including ssds and emmc.
Q: Which is a better option for high-speed data transfer, eMMC or SSD?
A: For high-speed data transfer, a PCIe NVMe SSD is generally better than eMMC.
Q: What type of storage device is an SD card?
A: An SD card is a type of memory card.
Q: Is eMMC storage better than traditional hard drives?
A: eMMC storage is better than traditional hard drives in terms of speed and efficiency.
Q: What is the difference between eMMC and SSD?
A: The difference between eMMC and SSD lies in their performance and use cases, with SSDs generally offering faster speeds and better performance.
Q: Can you explain what eMMC is?
A: eMMC is a type of flash memory and a flash storage solution that is commonly used in portable devices.
Q: What are NVMe SSDs known for?
A: NVMe SSDs are known for their high-speed data transfer capabilities.
Q: What is the function of an eMMC chip in devices?
A: An eMMC chip functions as the primary storage device in many mobile and portable devices.
Q: How does solid-state storage differ from traditional hard drives?
A: Solid-state storage, like SSDs and eMMC, uses flash memory instead of spinning disks, offering faster access times and better durability.
Q: What is the storage vs. speed comparison between eMMC and SSD?
A: In a storage vs. speed comparison, SSDs generally provide faster speeds and better performance compared to eMMC storage.
Q: What type of storage is commonly used in smartphones and tablets?
A: eMMC storage is commonly used in smartphones and tablets due to its compact size and adequate performance.
Q: How does an eMMC device differ from a traditional USB storage device?
A: An eMMC device is integrated directly onto the motherboard, unlike USB storage devices which are external.
Q: Is eMMC or SSD (solid-state drive) better for high-performance applications?
A: For high-performance applications, an SSD is typically better than eMMC.