Last Updated on April 28, 2024 by Arnav Sharma
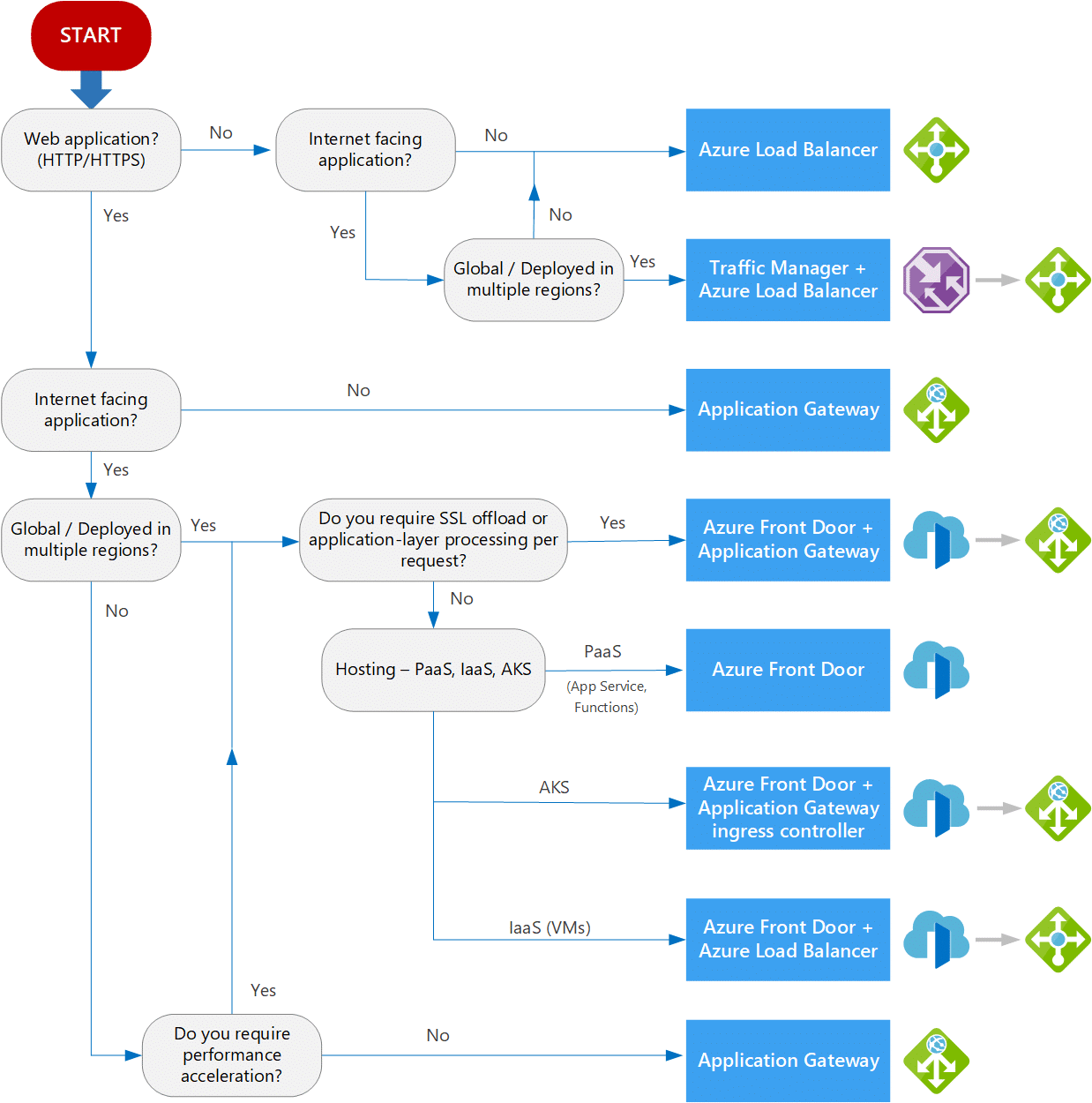
Azure offers a range of solutions to help you achieve optimal performance and scalability. Whether it’s the Azure Load Balancer, Application Gateway, or Traffic Manager, there are plenty of choices to suit your needs.
In this article, we’ll explore the different load balancing options available in Azure and provide you with some best practices to ensure a smooth and efficient load balancing experience.
Azure Load Balancer
You can utilize Azure Load Balancer to distribute network traffic across multiple virtual machines in your Azure environment. This load balancer enables you to achieve high availability and fault tolerance for your applications.
By evenly distributing incoming traffic, the load balancer ensures that no single virtual machine becomes overwhelmed with requests. It intelligently monitors the health of each virtual machine and automatically redirects traffic away from any unhealthy instances.
Azure Load Balancer supports both inbound and outbound scenarios, allowing you to balance traffic for incoming requests as well as manage outbound connections from your virtual machines. It also supports various protocols such as TCP, UDP, and HTTP, making it flexible for different application requirements.
With Azure Load Balancer, you can easily scale your applications and improve their performance and reliability in your Azure environment.
Application Gateway
An application gateway is a powerful tool that allows you to efficiently distribute network traffic to multiple backend servers in your Azure environment. It acts as a load balancer and provides various functionalities such as SSL termination, URL-based routing, and session affinity.
With the application gateway, you can improve the performance and availability of your applications by evenly distributing traffic across backend servers. It supports both HTTP and HTTPS protocols, making it suitable for hosting web applications. Additionally, the application gateway offers advanced features like web application firewall (WAF) and intelligent web application routing.
You can easily configure and manage the application gateway using Azure portal, PowerShell, or Azure CLI.
Traffic Manager
When implementing load balancing in Azure, consider using Traffic Manager to effectively distribute incoming network traffic to multiple backend resources.
Traffic Manager is a DNS-based load balancer that allows you to control the distribution of traffic to different endpoints based on various routing methods.
With Traffic Manager, you can leverage geographic routing to direct users to the nearest available endpoint, ensuring low latency and optimal performance.
You can also use performance routing to distribute traffic based on endpoint responsiveness, or even implement weighted round-robin routing to balance the load evenly across all endpoints.
Additionally, Traffic Manager provides automatic failover capabilities, allowing it to redirect traffic to healthy endpoints in the event of an outage.
Load Balancing Considerations
Take into account the different load balancing considerations when choosing the appropriate option for your Azure environment.
First, consider the type of traffic you’ll be handling. If your application requires high availability and redundancy, then using Azure Traffic Manager or Azure Load Balancer is recommended.
Next, consider the scalability requirements of your application. If your application needs to handle a large number of incoming requests, then Azure Application Gateway or Azure Front Door can provide the necessary scalability features.
Additionally, think about the geographic distribution of your users. Azure Traffic Manager can help you route traffic to the closest available endpoint based on the user’s location.
Lastly, consider the cost implications of each load balancing option. Some load balancing options may be more cost-effective depending on your specific requirements and budget.
Best Practices for Load Balancing in Azure
To ensure optimal performance and reliability, it’s essential that you regularly monitor and adjust your load balancing configuration in Azure. Here are some best practices to follow:
1. Use health probes: Configure health probes to regularly check the status of your backend instances. This helps identify any unhealthy instances and ensures that traffic is only routed to healthy instances.
2. Implement autoscaling: Set up autoscaling to automatically adjust the number of instances based on demand. This ensures that your application can handle increased traffic without any performance degradation.
3. Use traffic routing methods: Azure offers various traffic routing methods, such as round-robin, weighted, or performance-based routing. Choose the appropriate method based on your application’s requirements.
4. Monitor performance: Regularly monitor the performance of your load balancer and backend instances. Identify any bottlenecks or performance issues and take corrective actions.
In conclusion, when it comes to load balancing options in Azure, you have various choices such as Azure Load Balancer, Application Gateway, and Traffic Manager. Each option offers different features and capabilities to help distribute network traffic efficiently. However, it’s important to consider load balancing considerations and follow best practices to ensure optimal performance and availability in your Azure environment.
FAQ – Load-Balancing Options
Q: What is load-balancing?
A: Load balancing is a technique used to distribute network traffic across multiple servers or resources to ensure high availability and optimal performance.
Q: How does load-balancing work in Azure?
A: Azure provides load-balancing services that distribute incoming traffic to virtual machines or resources within a virtual network. It balances the traffic load to ensure efficient resource utilization.
Q: What are the load-balancing options in Azure?
A: Azure offers several load-balancing options, including Azure Load Balancer, Azure Application Gateway, and internal load balancer. These options provide different functionalities and can be used depending on the specific requirements.
Q: What is Azure Load Balancer?
A: Azure Load Balancer is a load-balancing service that distributes incoming network traffic across multiple virtual machines within a virtual network. It operates at the transport layer (Layer 4) of the OSI model.
Q: What is Azure Application Gateway?
A: Azure Application Gateway is a load-balancing service that operates at the application layer (Layer 7) of the OSI model. It provides advanced load-balancing functionalities and can be used for SSL termination, URL-based routing, and session affinity.
Q: How can I create a load-balancer in Azure?
A: To create a load balancer in Azure, you can use the Azure portal. Simply navigate to the Load Balancers section, click on “Add” button, and follow the step-by-step instructions to configure the load balancer according to your requirements.
Q: What is a virtual network in Azure?
A: A virtual network in Azure is a logically isolated network infrastructure that allows you to securely connect and manage your virtual machines and other resources. It provides communication and networking capabilities within the Azure cloud.
Q: What are azure load-balancing rules?
A: Load-balancing rules are configurations that define how the load balancer distributes incoming traffic to backend resources. These rules define the load-balancing algorithm, protocol, port, and other parameters.
Q: How can I use Azure Load Balancer?
A: You can use Azure Load Balancer by configuring load-balancing rules in the Azure portal. By defining the right load-balancing settings, you can distribute traffic across virtual machines or resources in a balanced manner, ensuring high availability and scalability.
Q: What is the Azure Architecture Center?
A: The Azure Architecture Center is a resource provided by Microsoft Azure that offers architectural guidance, best practices, and reference designs for building efficient and scalable solutions in Azure. It includes documentation, case studies, and architecture patterns.
keywords: sql ip address and port for azure load balancing in public load balancer and standard load balancer for layer 7 load balance traffic