Last Updated on April 20, 2024 by Arnav Sharma
IPConfig is a powerful command-line tool used to display and configure network adapter information on a Windows operating system. It provides valuable insights into IP addresses, DNS settings, DHCP configurations, and much more. In this article, we will explore the various features and options of IPConfig and how they can be used for troubleshooting network connectivity and configuring network settings.
What is ipconfig and how to use it?
Using the ipconfig command
The ipconfig command is used in the command prompt to display the current IP configuration of all network adapters on a Windows system. By simply entering “ipconfig” in the command prompt and pressing Enter, you can quickly access valuable network information.
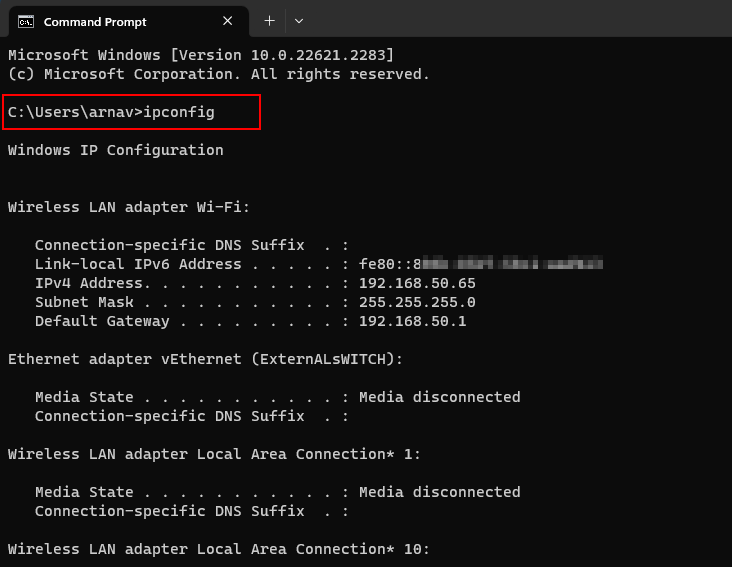
Command line options for ipconfig
IPConfig offers various command line options to retrieve specific information. For example, running “ipconfig /all” will display detailed configuration information for all network adapters, including DHCP and DNS settings. Other useful options include “/release” to release the current IP address, “/renew” to request a new IP address, and “/displaydns” to view the contents of the DNS resolver cache.
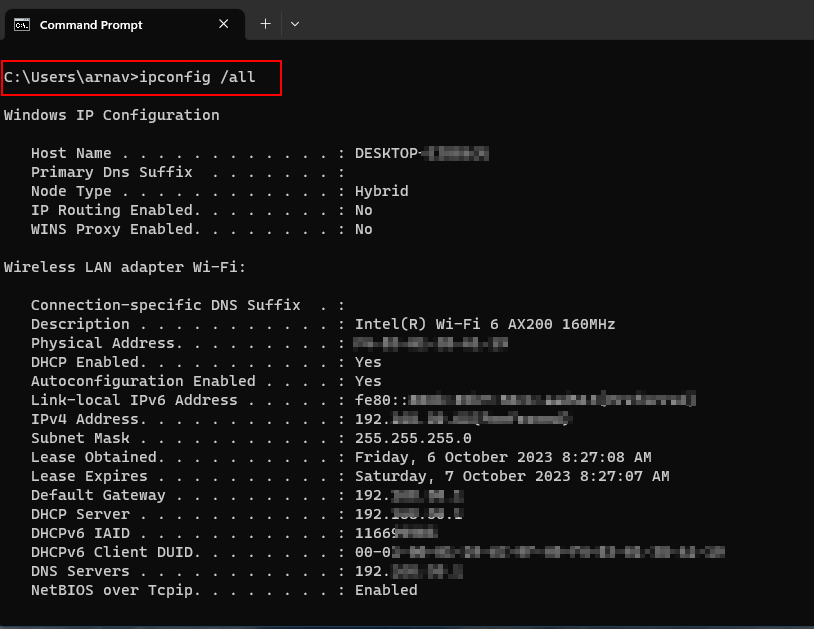
Using ipconfig in the command prompt
To use IPConfig, open the command prompt by searching for “cmd” in the Start menu or pressing Win + R and entering “cmd”. Once the command prompt opens, type “ipconfig” and press Enter to display the IP configuration for all network adapters on your system.
How does ipconfig display network adapter information?
Viewing IPv6 address using ipconfig
IPConfig allows you to view the IPv6 address assigned to your network adapter. By running “ipconfig /all” and looking under the adapter settings, you can find the IPv6 address and other useful details such as the default gateway, subnet mask, and DNS server addresses.

Checking DNS settings with ipconfig
With IPConfig, you can easily check the DNS settings of your network adapter. Running “ipconfig /all” will display the DNS server addresses assigned to your adapter. This information is crucial for troubleshooting DNS-related issues and ensuring smooth internet connectivity.
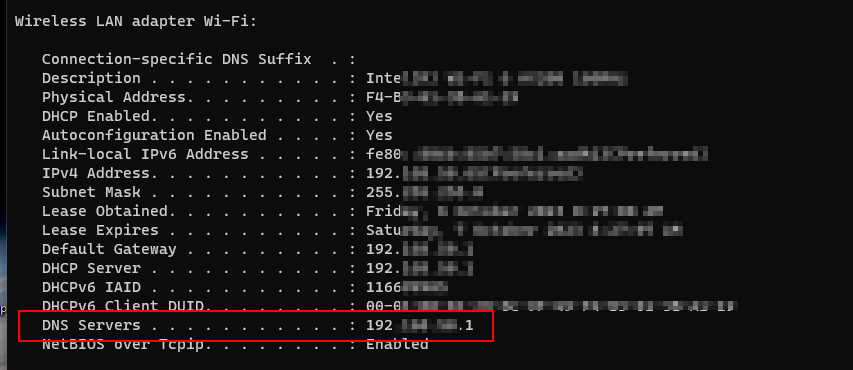
Understanding the DNS resolver cache with ipconfig
IPConfig provides insights into the DNS resolver cache, which stores information about previously resolved DNS queries. By running the command “ipconfig /displaydns”, you can view the DNS resolver cache and check the associated records, including the DNS names and IP addresses.

How can ipconfig help with troubleshooting network connectivity?
Examining the MAC address with ipconfig
IPConfig allows you to examine the MAC (Media Access Control) address of your network adapter. Running “ipconfig /all” will display the MAC address, which is a unique identifier used to identify a network adapter on a physical network. This information can be valuable for troubleshooting network connectivity issues.

Releasing and renewing IP addresses with ipconfig
In situations where you need to obtain a new IP address or resolve IP conflicts, IPConfig offers the “/release” and “/renew” options. Running “ipconfig /release” will release the current IP address, while “ipconfig /renew” will request a new IP address from the DHCP server. This can be particularly useful in troubleshooting connectivity problems.

Working with IPv4 addresses in ipconfig
IPv4 addresses play a vital role in network connectivity. IPConfig allows you to view the IPv4 address assigned to your network adapter with the command “ipconfig”. In addition, running “ipconfig /all” will provide detailed information about the IPv4 configuration, including the subnet mask, default gateway, and DHCP server.

How to configure network settings using ipconfig?
Setting default gateway with ipconfig
IPConfig allows you to configure the default gateway, which determines the path for network traffic to exit your local network. By entering “ipconfig /all” and locating the network adapter settings, you can specify the default gateway address using the “Default Gateway” field.
Configuring DHCP server with ipconfig
IPConfig provides the capability to configure the DHCP server, which automatically assigns IP addresses to network adapters. By running “ipconfig /all” and examining the DHCP server field, you can identify the DHCP server address and troubleshoot any DHCP-related issues.

Managing subnet mask with ipconfig
The subnet mask is used to distinguish between the network and host parts of an IP address. IPConfig allows you to manage the subnet mask by displaying it with the command “ipconfig” or “ipconfig /all”. This information is essential for network configuration and troubleshooting subnet-related problems.

What other information can ipconfig provide?
Viewing DNS server information with ipconfig
With IPConfig, you can easily view the DNS server information assigned to your network adapter. Running “ipconfig /all” will display the DNS server addresses. This information is crucial for ensuring proper DNS resolution and internet connectivity.

Examining the network interface using ipconfig
IPConfig provides detailed information about the network interface, including the adapter name, physical address (MAC address), and configuration information. By running “ipconfig /all”, you can gather valuable insights into your network adapter and troubleshoot network-related issues effectively.
List of Commands:

FAQ – Use IPConfig and IFConfig
Q: How can you view your network configuration, including your IP address, on a Linux system?
A: On a Linux system, you can view your network configuration and IP address by using the ifconfig command. This command displays information about all active network adapters on your computer, including their IP configuration, which consists of the IP address (both IPv4 and IPv6), subnet mask, and default gateway.
Q: What command is used on Microsoft Windows to obtain information about your IP configuration and refresh DHCP leases?
A: On Microsoft Windows, the ipconfig command is used to obtain information about your IP configuration and refresh DHCP leases. This command displays your IP address, subnet mask, default gateway, and DNS servers. It can also be used to renew your IP address and refresh all DHCP leases and DNS settings.
Q: What are the differences between using a static IP address and obtaining an IP address through DHCP?
A: The difference between using a static IP address and obtaining an IP address through DHCP (Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol) lies in how the IP address is assigned and managed. A static IP address is manually configured and remains constant, providing a consistent and unchanging IP address for a device. On the other hand, DHCP automatically assigns IP addresses from a pool, allowing for dynamic allocation and management of IP addresses. DHCP leases an IP address to a device for a specific period, after which the lease can be renewed or a new IP address can be assigned.
Q: What is the role of DNS (Domain Name System) in IP configuration?
A: The Domain Name System (DNS) plays a crucial role in IP configuration by translating human-readable domain names into numerical IP addresses that computers use to communicate over the Internet. This process allows users to access websites and other resources on the internet by using easily remembered names, like www.example.com, instead of having to remember the numerical IP address associated with that site.
Q: How can you renew your IP address and refresh your network settings on a Windows computer?
A: To renew your IP address and refresh your network settings on a Windows computer, you can use the ipconfig command with specific switches. For instance, ipconfig /release followed by ipconfig /renew will release your current DHCP lease and then obtain a new IP address from your DHCP server. Additionally, ipconfig /flushdns can be used to clear the DNS cache, ensuring that your computer keeps no local cache of old IP addresses and DNS records, which can help in resolving issues related to incorrect or outdated DNS information.
Q: What are the benefits of using DHCP for IP address configuration?
A: Using DHCP for IP address configuration offers several benefits, including automatic assignment of IP addresses, efficient management of IP address space, and ease of network administration. DHCP allows devices to obtain an IP address automatically, reducing the need for manual configuration and the risk of IP conflicts. It also supports automatic renewal of IP addresses, which simplifies the process of managing network configurations, especially in environments with a large number of networked devices.
Q: How can you view and manage your network configuration on a Mac OS system?
A: On a Mac OS system, you can view and manage your network configuration through the System Preferences under the Network section. Additionally, the ifconfig command can be used in the Terminal to display detailed information about your network interfaces, including IP addresses. For more advanced configuration, such as renewing DHCP leases or changing IP settings, Mac OS also supports using the ipconfig command in the Terminal, similar to its usage in Microsoft Windows, to manage network configuration values and refresh DHCP and DNS settings.
Q: What command on Windows is used to display the full configuration of all active network interfaces?
A: The ipconfig /all command on Windows is used to display the full configuration of all active network interfaces. This command provides detailed information about the network configuration, including IP address, subnet mask, default gateway, DHCP status, and DNS servers. It is useful for troubleshooting network issues or for obtaining detailed network configuration values.
Q: How do you manually set a static IP address on a Linux system?
A: To manually set a static IP address on a Linux system, you typically edit the network configuration file for your specific network interface. This involves specifying the static ip_address, subnet mask, and default gateway in the configuration file, and then restarting the network service or the computer to apply the changes. The exact process can vary depending on the Linux distribution and the network management tools it uses.
Q: What are the commands to view the IP address configuration and renew the DHCP lease on both Windows and Linux?
A: On Windows, the ipconfig command is used to view the IP address configuration, and ipconfig /renew is used to renew the DHCP lease. On Linux, the ifconfig command or ip addr show can be used to view IP address configuration. To renew the DHCP lease on Linux, you would typically use the dhclient command, which releases and then renews the DHCP lease for your network interface.
Q: How can you use command line interfaces to troubleshoot domain name resolution issues?
A: To troubleshoot domain name resolution issues using command line interfaces, you can use the nslookup command on both Windows and Linux. This command queries the Domain Name System (DNS) to obtain the IP address associated with a domain name or the domain name associated with an IP address. By examining the DNS records and ensuring they point to the correct IP address, you can identify and resolve issues related to domain name resolution.
Q: What is the significance of the DHCP class ID, and how is it used in network configuration?
A: The DHCP class ID is a unique identifier that can be used to differentiate between different types of devices or network configurations within the same DHCP scope. It allows DHCP servers to provide specific configuration parameters or IP address ranges to different classes of devices. By configuring DHCP class IDs, network administrators can manage and customize network configurations more efficiently, ensuring that devices receive appropriate network settings based on their class.
Q: How does a Windows computer refresh its network configuration and DHCP/DNS settings using the command line?
A: A Windows computer can refresh its network configuration and DHCP/DNS settings using the command line by employing the ipconfig /release command to release the current DHCP configuration and then ipconfig /renew to obtain a new IP address. Additionally, ipconfig /flushdns clears the local DNS resolver cache, and ipconfig /registerdns refreshes all DHCP leases and re-registers DNS names, ensuring the computer’s network settings are updated and any stale records are removed.
Q: What is an automatic private IP address, and when is it used?
A: An automatic private IP address (APIPA) is a self-assigned IP address used by Microsoft Windows when a DHCP server is not available. APIPA addresses are in the 169.254.0.1 to 169.254.255.254 range, allowing a device to communicate with other devices on the same local network segment but not with external networks. This mechanism ensures network communication can continue on a limited basis until DHCP services are restored.
internet protocol command is used to display command is used to display
