Last Updated on October 20, 2024 by Arnav Sharma
In today’s rapidly evolving digital landscape, organizations face unprecedented cybersecurity challenges. The growing sophistication of cyber threats, coupled with a shortage of skilled professionals in the cybersecurity field, has created a critical need for innovative solutions. Microsoft Copilot for Security—an AI-powered, cloud-based security analysis tool that aims to revolutionize the way organizations handle cybersecurity. But what is Microsoft Copilot for Security, and how does it work? Let’s dive deeper into the foundational aspects of this powerful tool.
What is Microsoft Copilot for Security?
Microsoft Copilot for Security is designed to assist security analysts by automating complex tasks and providing valuable insights through natural language processing. At its core, Copilot leverages large language models (LLMs) to process security signals and respond to threats with unprecedented speed and accuracy. This tool is more than just an automated response system—it is an intelligent assistant that helps security teams detect, analyze, and respond to threats more efficiently.
One of the primary goals of Microsoft Copilot is to bridge the gap between overwhelming amounts of security data and the limited resources available to analyze and act on that data. By enabling security analysts to work at machine speed, Copilot empowers organizations to mitigate risks faster and more effectively.
The Role of Generative AI in Microsoft Copilot
The backbone of Microsoft Copilot for Security is generative AI, a cutting-edge branch of artificial intelligence. But what exactly is generative AI, and why is it crucial to Copilot’s success?
Generative AI refers to a subset of AI that focuses on creating original content based on a natural language input, also known as a prompt. This content can range from text and images to code, depending on the type of model and the input given. For example, a user might provide a prompt asking for an incident report summary or a detailed explanation of a suspicious script. Generative AI is capable of producing a coherent and contextually accurate response to these requests.
Microsoft Copilot utilizes large language models (LLMs) such as OpenAI’s GPT-4, which have been trained on vast datasets comprising public and licensed content. These models are designed to understand and generate human-like text, enabling them to analyze logs, detect patterns, and even translate technical scripts into plain language. Essentially, they mimic human-like intelligence by learning the relationships between words and generating meaningful responses.
Key Features and Capabilities of Microsoft Copilot for Security
To truly understand Microsoft Copilot, it’s essential to explore its core features and capabilities. These capabilities are designed to address common pain points faced by cybersecurity teams and streamline various critical tasks:
- Incident Summarization: One of Copilot’s standout features is its ability to distill complex security alerts into concise, actionable summaries. This feature saves analysts significant time and effort, allowing them to quickly grasp the nature of incidents and communicate effectively across the organization. It also reduces the cognitive load on analysts, enabling them to focus on higher-level decision-making.
- Impact Analysis: Copilot leverages AI-driven analytics to assess the potential impact of security incidents. This includes understanding which systems and data have been affected, prioritizing response efforts, and gaining a clearer picture of the organization’s overall risk exposure. By providing these insights, Copilot enables quicker and more strategic decision-making.
- Reverse Engineering of Scripts: In the face of increasingly sophisticated cyberattacks, reverse engineering is crucial for understanding malicious scripts and detecting patterns. Copilot excels in this area by automatically analyzing complex command-line scripts and translating them into clear, natural language explanations. This eliminates the need for manual reverse engineering, which can be time-consuming and error-prone.
- Guided Responses: Copilot provides actionable, step-by-step guidance for incident response, covering triage, investigation, containment, and remediation. This guidance includes deep links to recommended actions, helping analysts quickly execute the necessary steps. The result is a more organized and efficient incident response process.
Standalone and Embedded Experiences
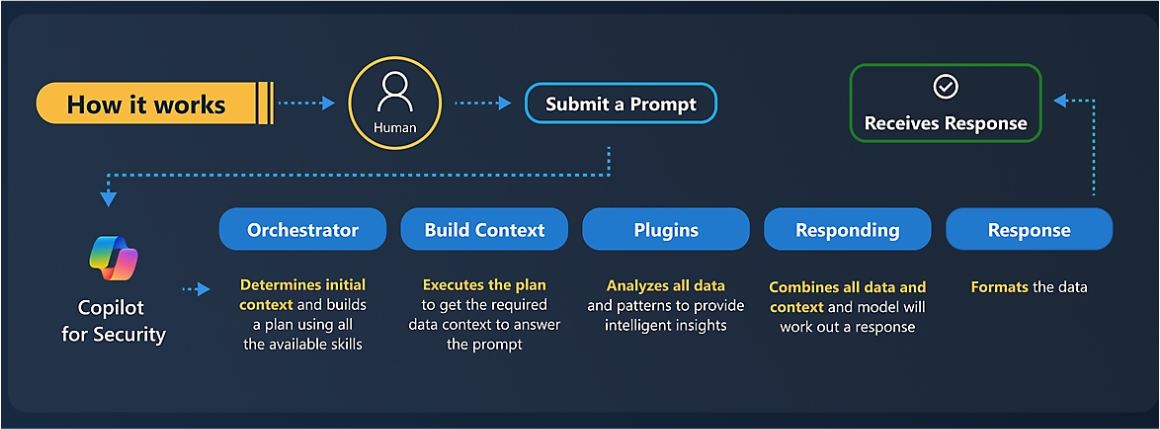
Microsoft Copilot for Security offers two primary modes of operation: the standalone experience and the embedded experience. In the standalone experience, Copilot is accessed through a dedicated portal. This allows users to interact directly with the tool using a natural language interface. Security analysts can submit specific prompts, such as requests for incident summaries or impact assessments, and receive detailed responses.
The embedded experience involves integrating Copilot’s capabilities directly into other Microsoft security products, such as Microsoft Sentinel and Microsoft Defender. This seamless integration allows analysts to access Copilot’s insights within the platforms they already use, reducing context-switching and streamlining their workflows.
For example, a security analyst using Microsoft Sentinel can leverage Copilot to generate a summary of an ongoing incident without leaving the Sentinel interface. This integration not only enhances productivity but also improves the user experience by providing a unified platform for security operations.
Why Microsoft Copilot for Security Matters
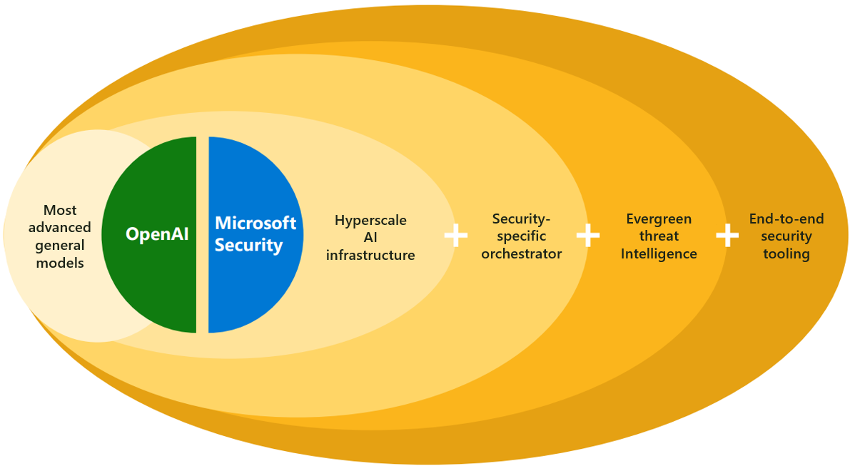
The introduction of Microsoft Copilot for Security represents a significant shift in how organizations can leverage AI to enhance their cybersecurity efforts. By combining the power of large language models with Microsoft’s security-specific models, Copilot enables security analysts to work more effectively and efficiently. Its ability to process data at machine speed, automate complex tasks, and provide actionable insights helps organizations stay ahead of emerging threats.
One of the most notable benefits of Microsoft Copilot is its accessibility. Thanks to its natural language interface, users of varying skill levels can interact with the tool and obtain valuable insights. This democratization of AI-driven security analysis is crucial in addressing the talent shortage in the cybersecurity field. Even organizations with limited resources can benefit from Copilot’s advanced capabilities, enabling them to build a more resilient security posture.
Conclusion
Microsoft Copilot for Security marks a new era of AI-powered cybersecurity solutions. By leveraging generative AI and large language models, Copilot enables organizations to detect, analyze, and respond to threats faster and more accurately than ever before. Understanding the foundational aspects of Microsoft Copilot—its purpose, technology, and core features—helps to unlock its potential for transforming cybersecurity operations.
As we move forward, it’s crucial for security professionals to explore how AI-powered solutions like Copilot can enhance their existing security frameworks. In the next blog, we will dive into the practical applications of Copilot and explore real-world use cases that demonstrate its impact on security operations.
FAQ:
Q: What is Microsoft Copilot for Security, and how does it work?
Microsoft Copilot for Security is an AI-powered security solution that integrates with other Microsoft security tools, such as Microsoft Defender XDR, Microsoft Intune, and Microsoft Entra. It provides security professionals with an assistive copilot experience designed to help improve security processes by enabling faster responses to threats. Copilot for Security works as a security analysis tool that enables professionals to leverage AI-powered security insights across Microsoft products.
Q: What are the key benefits of using Copilot for Security?
Copilot for Security provides a cybersecurity product that enables security professionals to respond efficiently to threats. It leverages AI for security by providing AI-powered security analysis tools, improving productivity with Copilot’s assistive experience, and integrating with other Microsoft security solutions. The key benefits include enhanced data security, speed and scale of AI, and responsible AI practices within Microsoft.
Q: What are the main use cases for Microsoft Copilot for Security?
Microsoft Copilot for Security helps improve security processes, enabling AI-powered security analysis and streamlining security updates. Key use cases include threat intelligence using Microsoft Defender Threat Intelligence, security training using Microsoft Learn, and ensuring compliance with data security standards through Microsoft Purview and Microsoft Security Services.
Q: How can customers get started with Microsoft Copilot for Security?
To get started with Microsoft Copilot for Security, customers need to join the Security Customer Connection Program. This program provides access to Copilot for Security, which is provisioned within the Copilot environment. Microsoft recommends using the integrated solutions across Microsoft, such as Microsoft Azure, Microsoft Defender, and Microsoft Entra, to ensure a comprehensive approach to security.
Q: How does AI play a role in Microsoft Security solutions?
AI for Security is central to Microsoft’s approach, providing speed and scale of AI across its security tools. AI-powered security enables proactive threat detection, data security, and AI-powered security analysis. Products like Microsoft Defender and Microsoft 365 Copilot leverage AI capabilities to deliver AI-powered security solutions and enhance security and compliance.
Q: What Microsoft tools integrate with Copilot for Security?
Copilot for Security integrates with several Microsoft tools, including Microsoft Defender XDR, Microsoft Intune, Microsoft Purview, Microsoft Entra, and Microsoft Azure. This integration enables a unified security approach and provides access to productivity tools within Microsoft Security solutions, making it a comprehensive solution for security professionals.