Last Updated on April 12, 2024 by Arnav Sharma
The registry is a system-defined database in which applications and system components store and retrieve configuration data. The data stored in the registry varies according to the version of Microsoft Windows. The kernel, device drivers, services, SAM, user interface and third-party applications can all make use of the registry.
There are five predefined root keys in Windows 8:
- HKEY_CLASSES_ROOT
- HKEY_CURRENT_USER
- HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE
- HKEY_USERS
- HKEY_CURRENT_CONFIG
1. HKEY_CLASSES_ROOT
HKEY_CLASSES_ROOT contains information about registered applications, such as file associations and OLE Object Class IDs, tying them to the applications used to handle these items. The file type subkeys in HKEY_CLASSES_ROOT have the same name as the file name extension for the file type, such as .exe. File type associations are stored in the registry, but you should use Windows Explorer to change them.
2. HKEY_CURRENT_USER
The HKEY_CURRENT_USER key is a link to the subkey of HKEY_USERS that corresponds to the user; the same information is accessible in both locations. On Windows NT-based systems, each user’s settings are stored in their own files called NTUSER.DAT and USRCLASS.DAT inside their own Documents and Settings subfolder. The mapping between HKEY_CURRENT_USER and HKEY_USERS is per process and is established the first time the process references HKEY_CURRENT_USER. The mapping is based on the security context of the first thread to reference HKEY_CURRENT_USER. If this security context does not have a registry hive loaded in HKEY_USERS, the mapping is established with HKEY_USERS.Default.
3. HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE
Registry entries subordinate to this key define the physical state of the computer, including data about the bus type, system memory, and installed hardware and software. It contains subkeys that hold current configuration data, including Plug and Play information, network logon preferences, network security information, software-related information, and other system information.
4. HKEY_USERS
Registry entries subordinate to this key define the default user configuration for new users on the local computer and the user configuration for the current user.Each time a new user logs on to a computer, a new hive is created for that user with a separate file for the user profile. This is called the user profile hive. A user’s hive contains specific registry information pertaining to the user’s application settings, desktop, environment, network connections, and printers. User profile hives are located under the HKEY_USERS key.
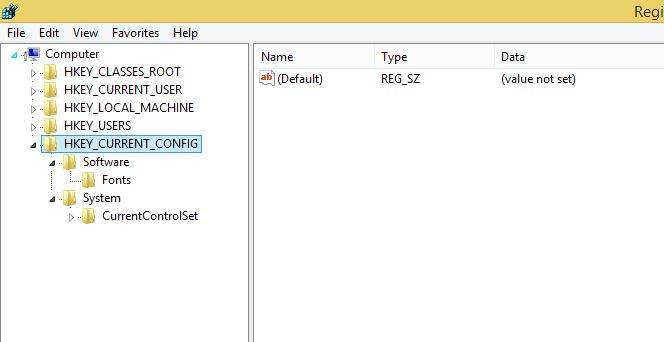
5. HKEY_CURRENT_CONFIG
Contains information about the current hardware profile of the local computer system. The information under HKEY_CURRENT_CONFIG describes only the differences between the current hardware configuration and the standard configuration.
FAQ – Windows Registry Editor
Q: What is the Windows Registry?
A: The Windows Registry is a hierarchical database that stores configuration settings and options for the Windows operating system.
Q: How do I open the Windows Registry?
A: To open the Windows Registry, you can use the Windows Registry Editor, which is a built-in tool in the Windows operating system.
Q: What is a registry key?
A: A registry key is a container that stores configuration settings and information in the Windows Registry. It is similar to a folder that holds multiple values.
Q: How can I edit the Windows Registry?
A: You can edit the Windows Registry by using the Windows Registry Editor. It allows you to modify or delete registry keys and values to make changes to the operating system’s configuration.
Q: What is a registry value?
A: A registry value is a specific piece of data stored within a registry key. It can hold various types of information, such as numbers, text, or binary data.
Q: How do I back up my registry?
A: To back up your registry, you can use the Windows Registry Editor to export the entire registry or specific registry keys and values to a file. This backup file can be used to restore the registry if any issues arise.
Q: Can I use the Windows Registry to make changes to my operating system?
A: Yes, you can use the Windows Registry to make changes to your operating system’s configuration settings. However, it is important to be careful when making changes as incorrect modifications can cause system instability or errors.
Q: Is it recommended to use a registry cleaner?
A: The usefulness of registry cleaners is a matter of debate. While they claim to improve system performance by removing unnecessary entries, they can also remove valid or necessary entries, which may lead to system issues. It is recommended to use caution when using registry cleaners.
Q: What versions of Windows have a registry file?
A: The Windows Registry is a feature found in various versions of the Windows operating system, including Windows 95, Windows 98, Windows XP, Windows Vista, Windows 7, Windows 8, Windows 10, and Windows 11.
Q: What kind of information does the registry contain?
A: The registry contains configuration settings, options, and other information related to the Windows operating system and installed software. It stores data in the form of registry keys and values.
Q: How can one edit the registry in the Microsoft Windows operating system?
A: To edit the registry, you would typically open the registry editor, which provides an interface to view and make changes to the windows registry. The windows registry is a database that stores configurations for the Microsoft Windows operating system, including software and windows settings.
Q: Why is backing up your registry important before making changes?
A: Backing up the registry is crucial because incorrect changes to the windows registry can lead to system malfunctions or other registry errors. Having a backup of the registry allows you to restore the windows settings and other configurations to a previous state, preventing potential issues or system crashes.
Q: How does the registry function in the Microsoft Windows operating system?
A: The registry in the Microsoft Windows operating system is like a database that contains software and windows settings, configuration details, and other data linked to the registry hive. It’s structured with branches, keys, and values. The structure of the registry is hierarchical, with each registry key preloaded with subkeys and values.
Q: What should be considered when making changes to the registry?
A: When making changes to the registry, one should be cautious because incorrect edits can lead to broken registry items or system malfunctions. Always back up the registry before making any changes, ensure that you understand the implications of the changes, and use the registry editor with caution.
Q: Can you describe the historical significance of the registry in Microsoft Windows?
A: The registry was introduced with the release of Windows 95, replacing the older INI files that were previously used for configuration. Over the years, the Windows registry has evolved and expanded, with newer versions of Microsoft Windows operating systems providing enhanced capabilities and functionalities. However, legacy windows registry API functions from earlier versions like windows 9x or windows 3.1 are still recognized by newer systems.
Q: Why are configuration files sometimes linked to the registry?
A: Configuration files, such as INI files, were the predecessors to the registry in earlier versions of Windows. As Windows evolved, the registry became the primary database for system and application settings, but some applications and parts of the system might still reference or use these older configuration methods, either for backward compatibility or specific functions.
Q: How can one safely use the registry without causing system issues?
A: To safely use the registry:
- Always create a backup of the registry before making changes.
- Avoid making changes unless you are certain of their implications.
- Use the registry editor cautiously and ensure you know the content of a registry key before altering it.
- Avoid using third-party registry cleaning tools unless they are well-reviewed and trusted.
- Understand that the registry values may contain backslashes and other special characters that need to be entered correctly.
Q: What’s the relationship between the user interface and the registry?
A: The Windows user interface often reflects the settings and configurations stored in the registry. Changes made to the registry can directly affect the appearance, behavior, and functionalities in the Windows user interface. Conversely, some adjustments made through the windows user interface are reflected as changes in the registry values and keys.
Q: What are registry settings and how can they be accessed inside the registry?
A: Registry settings refer to configurations and data stored inside the registry, which is a hierarchical database that the Windows operating system uses to store configuration information. To access these settings, one would typically use an editor on windows known as the registry editor.
Q: How can changes be made to the registry, especially to a particular registry key?
A: Changes to the registry can be done using the registry editor. A specific registry key may be located and edited directly within this tool. However, it’s crucial to ensure any edits are accurate as incorrect changes can result in system malfunctions.
Q: Can you describe the structure and elements inside the registry?
A: The registry is structured with various branches of the registry, including keys, subkeys, and values. Each registry key may have multiple subkeys and values associated with it. These values are generally named by their windows API definitions. Each registry value stored within a key has a specific data type and information, which influences how the Windows system or applications operate.
Q: Is it possible to have references to another registry within the registry?
A: Yes, inside the registry, a registry key or value might reference another registry key. This interlinking allows for a more organized and structured way of storing configuration data.
Q: What are the implications of using some legacy windows registry functions in modern systems?
A: Using some legacy windows registry functions on contemporary systems can result in compatibility issues. Older API functions or methods might not be supported or could behave differently on newer versions of Windows. Therefore, it’s crucial to ensure that any legacy functions used are compatible with the current windows system setup.
Q: How is the naming convention managed in the registry?
A: The name part of each registry key or value is generally named by their windows API definitions. The specificity ensures consistency and clarity when software or the system references these keys or values.
Q: What are some of the common file types associated with the registry?
A: One of the common file types associated with the registry is the .reg file. This file type is used to export, backup, or import registry entries, allowing for easy transfer or recovery of registry data.